Thermal Oil Heaters


- Standard vertical and horizontal construction.
- High temperatures up to 300°C at atmospheric pressure.
- Suitable for oil and gas as fuel.
- Suitable for water, mineral and synthetic oil.
- Optional temperature level set-points.
- Low film temperature, ensures long life of the thermal fluid.
- Easy to operate and fully automatic operation.
- Low maintenance cost.
- Clean and safety in operation.
- Profitable installation costs (low pressure system).
- Low thermal fluid resistance.
- High flue gas velocity, resulting in a good heat transfer.
- High efficiency consumption (up to 88%).
- Triple draw flue gas principle.
- Removable front cover.
- Front resistant (up to -30°C).
- Gas-tight welded inner jacket on all heaters.
- Thick insulated jacket minimises radiation loss.
- Outer jacket of steel plate.
(As option we can offer an inspection hole.)
ADVANTAGES OVER STEAM
- No corrosion and no risk of freezing damages.
- Without Water Treatment (thermal oil can be used for years).
- Quiet in operation (no steam stroke and flash steam noise).
- Operation nearly pressure less.
- Easy to operate (does not require a steam boiler certified staff).
- No equipment for pre-treatment of boiler feed water.
- Possibility of indirect hot water and steam generation.
| Design Data | ||
|---|---|---|
| Type | Fired thermal fluid heater | |
| Execution | Cylindrical Horizontal or Cylindrical Vertical | |
| Size | 100 - 20,000 kW | |
| Design Code | ASME VIII Div. 1 | |
| Efficiencies | 84-87% | |
| Pressure | 10 / 13 bar (g) | |
| Temperature | 100 / 370º C | |
| Fuels | Natural Gas, Light Fuel Oil, Heavy Fuel Oil and Combinations (duel fuel) |
|
| Burner | Monoblock pressure jet burner | |
| Rotary cup burner | ||
Thermal Oil Heaters are used in the following industries:
- Gold Mining Industry - for extracting gold.
- Metal Processing Industry - for pickling baths, varnishing plants, degreasing systems.
- Chemical Industry - for autoclaves, reaction tanks, mixing plants.
- M.D.F. Board Manufacturers - paper - pasteboard Industry - wood or laminate presses, hot presses, chip board pressers, dryers.
- Construction Material Industry - for heating of form works, brick works, dry chambers.
- Tar Manufacturing Industry - for roofing felt plants, store and mixing installations, tank depots.
- Food Industry - for baking plants, distilling, fat-splitting, pasteurising.
- Textile Industry - coating, colouring, clalanders, stenters, dryers and hot flues.
- Soap and Detergent Industry - for autoclaves, spray and drying columns, soaping plants.
- General Heating Applications.

Illustration above: Comparing different kind of thermal oil types, water and steam .
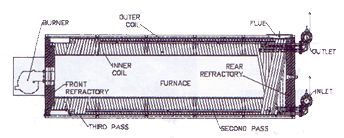
CONSTRUCTIONThe heaters are made with coils of seamless tubes. The heater consists of a tubular coil through which a regulated oil flow is pumped. This coil is arranged in two sections, inner and outer. The inner coil forms the combustion chamber (furnace) where radiant and convection heat transfer occurs. The area between the inner and outer coil and the area between the outer coil and supporting case form the flue gas passes where convection heat transfer occurs, cooling the combustion gases to the required temperature prior to the flue outlet. Heat transfer to the oil takes place in these tubes, which form the inner and outer coil. The oil enters the heater via the inlet header passing to the outer coil through the inner coil. The heated oil flows to the inner coil outlet then onto the outlet header through to the system pipe work.
 SAFETY
SAFETY
- The flow switch, which monitors the flow of oil into the generating coil.
- The oil level switch located in the system expansion tank, which monitors the system oil level.
- The stack and high limit overheat thermostats, which monitor the generating coil operating temperature.
- Safety valves, which ensure that the heater does not become over pressurised.
- Cold start thermostat reduces burner capacity until the minimum viscosity of thermo oil is being reached.
- Combustion is blocked until the pump is running properly.
- Flow monitoring by type-tested differential pressure system.
- If the minimum flow falls short the burner stops at once.
- All safety appliance in addition give optical and acoustic alarm. The source of error is shown at the colour cabinet.
